Early detection and treatment of postpartum haemorrhage: The E-MOTIVE project
Project Details
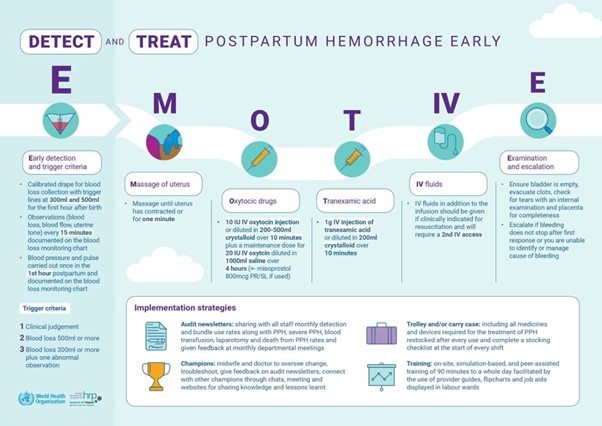
Postpartum haemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal death, accounting for 27% of maternal deaths worldwide. Delays in the detection or initiating treatment of postpartum haemorrhage can result in complications or death.
Despite strong efforts to adopt and scale up use of evidence-based interventions to prevent, detect, and treat PPH, three critical challenges remain. First, PPH is often undetected or detected late, leading to treatment delays. Second, when PPH does occur, there is often delayed or inconsistent use of life-saving interventions. Third, there is poor uptake of existing prevention and treatment guidelines at the point-of-care.
The E-MOTIVE project, led by the University of Birmingham and in collaboration with the Nossal’s Gender and Women’s Health team, aimed to address these three challenges through a multi-component strategy to:
- improve early detection of PPH by using a calibrated blood loss collection drape,
- implement a first response treatment bundle to be delivered in quick succession and consisting of uterine massage, oxytocic drugs, tranexamic acid, and a process for examination and escalation if bleeding continued.
Delivery of the E-MOTIVE intervention was supported by implementation strategies including the use of PPH trolleys or carry cases, on-site simulation-based training, audit and feedback of actionable data, and local champions (midwives and doctors).
The E-MOTIVE trial showed a remarkable 60% reduction in postpartum haemorrhage in the four study countries: Kenya, Nigeria, South Africa and Tanzania.
Researchers
Associate Professor Meghan Bohren
Dr Shahinoor Akter
Collaborators
University of Birmingham
Funding
This project is supported by a grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Research Publications
- Randomized Trial of Early Detection and Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage
Trial results show a 60% reduction in postpartum haemorrhage outcomes. - Perceptions and experiences of the prevention, identification and management of postpartum haemorrhage: a qualitative evidence synthesis
Cochrane qualitative evidence synthesis that contributed to the new WHO guideline recommendations on postpartum haemorrhage detection and management. - Formative research to design an implementation strategy for a postpartum hemorrhage initial response treatment bundle (E-MOTIVE): study protocol
Study protocol for the formative research outlines the critical steps of mixed-methods formative research and co-design to design the E-MOTIVE trial and implementation strategies. - Detection and management of postpartum haemorrhage: Qualitative evidence on healthcare providers' knowledge and practices in Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa
Describes current practices of postpartum haemorrhage detection and management, to identify areas for improvement ahead of the E-MOTIVE trial roll-out. - Factors influencing postpartum haemorrhage detection and management and the implementation of a new postpartum haemorrhage care bundle (E-MOTIVE) in Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa
Mapping of key factors (barriers and facilitators) influencing postpartum haemorrhage detection and management, to implementation science frameworks (COM-B and Theoretical Domains Framework) to help shape implementation strategies.
Research Group
Gender and Women's Health Unit
School Research Themes
Disparities, disadvantage and effective health care
Key Contact
For further information about this research, please contact the research group leader.
MDHS Research library
Explore by researcher, school, project or topic.